Page 21 - Demo
P. 21
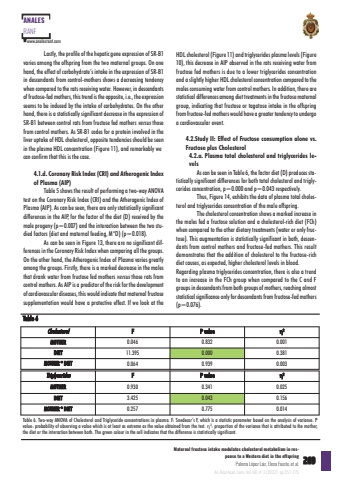
269ANALESRANFwwwanalesranfcomMaternalfructoseintakemodulatescholesterolmetabolisminresponsetoaWesterndietintheoffspringPalomaLópezLaizElenaFausteetalAnRealAcadFarmVol88nº3(2022)·pp257-275HDLcholesterol(Figure11)and triglyceridesplasmalevels(Figure10)thisdecreaseinAIPobservedintheratsreceivingwaterfromfructosefedmothersisduetoalowertriglyceridesconcentrationanda slightlyhigherHDLcholesterolconcentrationcompared to themalesconsuming water fromcontrolmothersInaddition therearestatisticaldifferencesamongdiet treatmentsin the fructosematernalgroupindicatingthatfructoseortagatoseintakeintheoffspringfrom fructose-fedmothers wouldhaveagreater tendency toundergoacardiovascularevent2StudyIIEffectofFructoseconsumptionalonevsFructoseplusCholesterol2aPlasmatotalcholesterolandtriglycerideslevelsAscanbe seenin Table6 the factordiet(D)produces statisticallysignificantdifferencesforbothtotalcholesterolandtriglyceridesconcentrationp=0000andp=0043respectively.ThusFigure14exhibitsthedataofplasmatotalcholesterolandtriglyceridesconcentrationofthemaleoffspringThecholesterolconcentrationshowsamarkedincreaseinthemalesfedafructosesolutionandacholesterol-richdiet(FCh)whencompared to theotherdietary treatments(wateroronly fructose)Thisaugmentationisstatisticallysignificantinbothdescendantsfromcontrolmothersandfructose-fedmothersThisresultdemonstratesthattheadditionofcholesteroltothefructose-richdietcausesasexpectedhighercholesterollevelsinbloodRegardingplasmatriglyceridesconcentrationthereisalsoatrendtoanincreaseintheFChgroupwhencomparedtotheCandFgroupsindescendants frombothgroupsofmothersreachingalmoststatistical significanceonly fordescendants from fructose-fedmothers(p=0076)Lastly, theprofileof thehepaticgeneexpressionofSR-B1variesamongtheoffspringfromthetwomaternalgroupsOnonehand theeffectofcarbohydratesintakein theexpressionofSR-B1indescendantsfromcontrol-mothersshowsadecreasingtendencywhencompared to theratsreceiving water.However,indescendantsof fructose-fedmothers this trendis theoppositeie theexpressionseemstobeinducedbytheintakeofcarbohydratesOntheotherhand thereisa statistically significantdecreasein theexpressionofSR-B1betweencontrolratsfromfructosefedmothersversusthosefromcontrolmothersAsSR-B1codesforaproteininvolvedintheliveruptakeofHDLcholesterolopposite tendenciesshouldbeseenintheplasmaHDLconcentration(Figure11)andremarkablywecanconfirmthatthisisthecase1dCoronaryRiskIndex(CRI) and AtherogenicIndexofPlasma(AIP)Table 5shows theresultofperforminga two-way ANOVAtestontheCoronaryRiskIndex(CRI)andtheAtherogenicIndexofPlasma(AIP) Ascanbeseen thereareonlystatisticallysignificantdifferencesintheAIP,forthefactorofthediet(D)receivedbythemaleprogeny(p=0007)and theinteractionbetween the twostudiedfactors(dietandmaternalfeedingM*D)(p=0018)AscanbeseeninFigure13therearenosignificantdifferencesin theCoronaryRiskIndex whencomparingall thegroupsOntheotherhandtheAtherogenicIndexofPlasmavariesgreatlyamongthegroupsFirstly,thereisamarkeddecreaseinthemalesthatdrankwaterfromfructosefedmothersversusthoseratsfromcontrolmothers As AIPisapredictorof therisk for thedevelopmentofcardiovasculardiseases this wouldindicate thatmaternal fructosesupplementationwouldhaveaprotectiveeffectIfwelookattheCholesterolFPvalueη2MOTHER004608320001DIET1139500000381MOTHER*DIET006409390003TriglyceridesFPvalueη2MOTHER093003410025DIET342500430156MOTHER*DIET025707750014Table6Table6Two-wayANOVAofCholesterolandTriglycerideconcentrationsinplasmaFSnedecorsF,whichisastatisticparameterbasedontheanalysisofvariancePvalueprobabilityofobservingavaluewhichisatleastasextremeasthevalueobtainedfromthetest2proportionofthevariancethatisattributedtothemother,thedietortheinteractionbetweenbothThegreencolourinthecellindicatesthatthedifferenceisstatisticallysignificant