Page 77 - 66_04
P. 77
VOL 66 (4) 2000 IN VITRO INDUCTION OF APOPTOSIS BY CYCLOSPORINE A
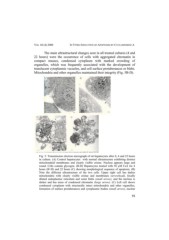
The main ultrastructural changes seen in all treated cultures (4 and
22 hours) were the occurrence of cells with aggregated chromatin in
compact masses, condensed cytoplasm with marked crowding of
organelles, which was frequently associated with the development of
translucent cytoplasmic vacuoles, and cell surface protuberances or blebs.
Mitochondria and other organelles maintained their integrity (Fig. 5B-D).
Fig. 5: Transmission electron micrograph of rat hepatocytes after 0, 4 and 22 hours
in culture. (A) Control hepatocytes with normal ultrastructure exhibiting distinct
mitochondrial membranes and clearly visible cristae. Nucleus appears large and
round. Cells contain glycogen. (B-D) Hepatocytes treated with 50 µM CsA for 4
hours (B+D) and 22 hours (C) showing morphological sequence of apoptosis. (B)
Note the different ultrastructure of the two cells. Upper right cell has darker
mitochondria with clearly visible cristae and membranes (arrowhead), focally
dilated endoplasmic reticulum and some blebs (small arrow), and the nucleus is
darker and has areas of condensed chromatin (large arrow). (C) Left cell shows
condensed cytoplasm with structurally intact mitochondria and other organelles,
formation of surface protuberances and cytoplasmic bodies (small arrow), nuclear
15