Page 92 - 82_02
P. 92
New therapeutic targets for the treatment of insulin resistance…
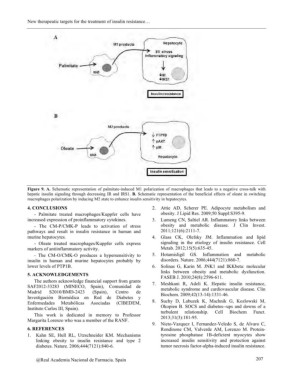
Figure 9. A. Schematic representation of palmitate-induced M1 polarization of macrophages that leads to a negative cross-talk with
hepatic insulin signaling through decreasing IR and IRS1. B. Schematic representation of the beneficial effects of oleate in switching
macrophages polarization by inducing M2 state to enhance insulin sensitivity in hepatocytes.
4. CONCLUSIONS 2. Attie AD, Scherer PE. Adipocyte metabolism and
- Palmitate treated macrophages/Kuppfer cells have obesity. J Lipid Res. 2009;50 Suppl:S395-9.
increased expression of proinflammatory cytokines. 3. Lumeng CN, Saltiel AR. Inflammatory links between
obesity and metabolic disease. J Clin Invest.
- The CM-P/CMK-P leads to activation of stress 2011;121(6):2111-7.
pathways and result in insulin resistance in human and
murine hepatocytes. 4. Glass CK, Olefsky JM. Inflammation and lipid
signaling in the etiology of insulin resistance. Cell
- Oleate treated macrophages/Kuppfer cells express Metab. 2012;15(5):635-45.
markers of antiinflammatory activity.
5. Hotamisligil GS. Inflammation and metabolic
- The CM-O/CMK-O produces a hypersensitivity to disorders. Nature. 2006;444(7121):860-7.
insulin in human and murine hepatocytes probably by
lower levels of PTP1B. 6. Solinas G, Karin M. JNK1 and IKKbeta: molecular
links between obesity and metabolic dysfunction.
5. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS FASEB J. 2010;24(8):2596-611.
The authors acknowledge financial support from grants 7. Meshkani R, Adeli K. Hepatic insulin resistance,
SAF2012-33283 (MINECO, Spain), Comunidad de metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease. Clin
Madrid S2010/BMD-2423 (Spain), Centro de Biochem. 2009;42(13-14):1331-46.
Investigación Biomédica en Red de Diabetes y
Enfermedades Metabólicas Asociadas (CIBEDEM, 8. Suchy D, Labuzek K, Machnik G, Kozlowski M,
Instituto Carlos III, Spain). Okopien B. SOCS and diabetes--ups and downs of a
turbulent relationship. Cell Biochem Funct.
This work is dedicated in memory to Professor 2013;31(3):181-95.
Margarita Lorenzo who was a member of the RANF.
9. Nieto-Vazquez I, Fernandez-Veledo S, de Alvaro C,
6. REFERENCES Rondinone CM, Valverde AM, Lorenzo M. Protein-
tyrosine phosphatase 1B-deficient myocytes show
1. Kahn SE, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM. Mechanisms increased insulin sensitivity and protection against
linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced insulin resistance.
diabetes. Nature. 2006;444(7121):840-6.
@Real Academia Nacional de Farmacia. Spain 207