Page 28 - 82_02
P. 28
kinase (40). In fact, experiments performed with PKR-/- María Ángel García Chaves
MEF showed that NF-?B activation was impaired in
response to pIC treatment. As a consequence of the NF-?B performed with human cells and vaccinia virus
activation impairment, PKR-/- MEF show defects in IFN recombinants expressing PKR in an inducible manner
(Figure 1), showing that I?Ba phosphorylation on serines
production compared with wt MEF (40). The first 32 and 36 precedes its degradation and translocation of
experiments to show the ability of PKR to activate NF-?B NF-?B to the nucleus (41, 42).
in the context of viral infection came from the laboratory
of Dr Esteban in 1999-2000. These experiments were
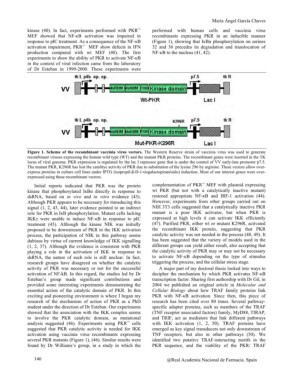
Figure 1. Scheme of the recombinant vaccinia virus vectors. The Western Reserve strain of vaccinia virus was used to generate
recombinant viruses expressing the human wild type (WT) and the mutant PKR proteins. The recombinant genes were inserted in the TK
locus of viral genome. PKR expression is regulated by the lac I repressor gene that is under the control of VV early-late promoter p7.5.
The mutant PKR, K296R has lost the catalityc activity of PKR due to substitution of the lysine 296 by arginine. These vectors allow over-
express proteins in culture cell lines under IPTG (isopropil-ß-D-1-tiogalactopiranósido) induction. Most of our interest genes were over-
expressed using these recombinant vectors.
Initial reports indicated that PKR was the protein complementation of PKR-/- MEF with plasmid expressing
kinase that phosphorylated I?Ba directly in response to wt PKR (but not with a catalytically inactive mutant)
dsRNA, based on in vivo and in vitro evidence (43). restored appropriate NF-?B and IRF-1 activation (44).
Although PKR appears to be necessary for transducing this However, experiments from other groups carried out on
signal (1, 2, 43, 44), later evidence pointed to an indirect NIH 3T3 cells suggested that a catalytically inactive PKR
role for PKR in I?B phosphorylation. Mutant cells lacking mutant is a poor IKK activator, but when PKR is
IKK? were unable to induce NF-?B in response to pIC expressed at high levels it can activate IKK efficiently
treatment (45). Although the kinase NIK was initially (47). Purified PKR, either wt or mutant K296R, activated
proposed to be downstream of PKR in the IKK activation the recombinant IKK protein, suggesting that PKR
process, the participation of NIK in this pathway seems catalytic activity was not needed in the process (48, 49). It
dubious by virtue of current knowledge of IKK signalling has been suggested that the variety of models used in the
(1, 2, 37). Although the evidence is consistent with PKR different groups can yield either result, also accepting that
playing a role in the activation of IKK in response to the catalytic activity of PKR may or may not be necessary
dsRNA, the nature of such role is still unclear. In fact, to activate NF-?B depending on the type of stimulus
research groups have disagreed on whether the catalytic triggering the process, and the cellular stress stage.
activity of PKR was necessary or not for the successful
activation of NF-kB. In this regard, the studies led by Dr A major part of my doctoral thesis looked into ways to
Esteban’s group made significant contributions and decipher the mechanism by which PKR activates NF-?B
provided some interesting experiments demonstrating the transcription factor. Sharing first authorship with Dr Gil, in
essential action of the catalytic domain of PKR. In this 2004 we published an original article in Molecular and
exciting and pioneering environment is where I began my Cellular Biology about how TRAF family proteins link
research of the mechanism of action of PKR as a PhD PKR with NF-?B activation. Since then, this piece of
student under the direction of Dr Esteban. Our experiments research has been cited over 80 times. Several pathway-
showed that the association with the IKK complex seems specific adapter proteins, such as members of the TRAF
to involve the PKR catalytic domain, as mutational (TNF receptor associated factors) family, MyD88, TIRAP,
analysis suggested (46). Experiments using PKR-/- cells and TRIF, act as mediators that link different pathways
suggested that PKR catalytic activity is needed for IKK with IKK activation (1, 2, 50). TRAF proteins have
activation using vaccinia virus recombinants expressing emerged as key signal transducers not only downstream of
several PKR mutants (Figure 1), (46). Similar results were TNF receptors, but also in other pathways (50). We
found by Dr Williams’s group, in a study in which the identified two putative TRAF-interacting motifs in the
PKR sequence, and the viability of the PKR/ TRAF
146 @Real Academia Nacional de Farmacia. Spain