Page 29 - 82_02
P. 29
A historical overview of protein kinase PKR… activation of Interferon type I, such as TLR-related
pathways (52). Recently PKR/TRAFs have been also
interaction was suggested by bioinformatic analysis and involved in the protection against a disease caused by a
confirmed in vivo (51). The interaction between PKR and non-viral pathogen (53).
TRAF2 or TRAF5 was shown to be dependent on PKR
dimerisation and is functionally relevant, as we 3.4. PKR involvement in different signalling pathways:
demonstrated in cells genetically deficient in TRAF2 and New PKR networks through microarray analysis
TRAF5 or after expression of TRAF dominant negative
molecules, suggesting that TRAF family proteins act The number of functions that PKR plays is in
downstream of PKR and signal towards the activation of correlation with its participation in numerous signalling
NF-?B (51). With our study as a starting point, other pathways that have been described over several studies (1,
groups have linked PKR/TRAF with several signalling 2, 26) (Figure 2).
pathways with significant relevance in the induction and
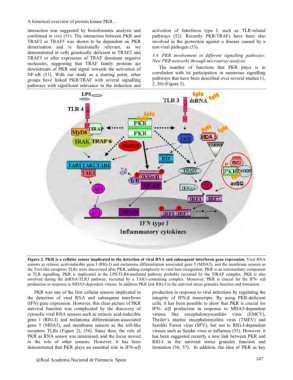
Figure 2. PKR is a cellular sensor implicated in the detection of viral RNA and subsequent interferon gene expression. Viral RNA
sensors as retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) and melanoma differentiation associated gene 5 (MDA5), and the membrane sensors as
the Tool-like receptors TLRs were discovered after PKR, adding complexity to viral host recognition. PKR is an intermediary component
in TLR signalling. PKR is implicated in the LPS/TLR4-mediated pathway probably recruited by the TIRAP complex. PKR is also
involved during the dsRNA/TLR3 pathway, recruited by a TAK1-containing complex. Moreover, PKR is crucial for the IFN- a/ß
production in response to MDA5-dependent viruses. In addition PKR link RIG-I in the antiviral stress granules function and formation.
PKR was one of the first cellular sensors implicated in production in response to viral infections by regulating the
the detection of viral RNA and subsequent interferon integrity of IFN-ß transcripts. By using PKR-deficient
(IFN) gene expression. However, this clear picture of PKR cells, it has been possible to show that PKR is crucial for
antiviral function was complicated by the discovery of IFN- a/ß production in response to MDA5-dependent
cytosolic viral RNA sensors such as retinoic acid-inducible viruses like encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV),
gene I (RIG-I) and melanoma differentiation-associated Theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus (TMEV) and
gene 5 (MDA5), and membrane sensors as the toll-like Semliki Forest virus (SFV), but not to RIG-I-dependent
receptors TLRs (Figure 2), (54). Since then, the role of viruses such as Sendai virus or influenza (55). However, it
PKR as RNA sensor was minimised, and the focus moved has been suggested recently a new link between PKR and
to the role of other sensors. However, it has been RIG-I in the antiviral stress granules function and
demonstrated that PKR plays an essential role in IFN-a/ß formation (56, 57). In addition, the idea of PKR as key
@Real Academia Nacional de Farmacia. Spain 147