Page 323 - 73_04
P. 323
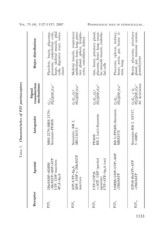
TABLE 1. Characteristics of P2Y purinoceptors VOL. 73 (4), 1127-1157, 2007
Receptor Agonist Antagonist Signal Major distribution
transduction
mechanisms
P2Y1 2MeSADP>ADPßS MRS 2279>MRS 2179> Gq/11 Platelets, brain, placenta,
>MeSATP=ADP>ATP prostate, endothelial cells,
Suramin>PPADS PLCß/IP3/Ca2+ heart, skeletal muscle, glial
UTP, UDP inactives cells, digestive tract, osteo-
clasts
AP3A>Ap2A
P2Y2 ATP˜UTP>Ap4A Suramin> RB 2, Gq/G11;Gi? Skeletal muscle, respiratory
P2Y4 ADP, UDP y 2MeSATP ARC126313 PLCß/IP3/Ca2+ epithelium, bone, lung, pitui-
P2Y6 inactives tary gland, spleen, lympho-
PPADS Gq/G11;Gi? cytes, osteoblasts, kidney PHYSIOLOGICAL ROLE OF EXTRACELLULAR...
UTP>UTP?S RB 2 (rat)>Suramin PLCß/IP3/Ca2+
>>ATP, UDP (partial Gut, brain, pituitary gland,
agonists) RB 2>PPADS>Suramin, Gq/G11 placenta, heart, lung, vascu-
UTP=ATP=Ap4A (rat) MRS2578 PLCß/IP3/Ca2+ lar smooth muscle, endothe-
lial cells
UDPßS>UDP>UTP>ADP
>2MeSATP Placenta, spleen, kidney,
heart, aorta, gut, brain, ti-
mus, lung.
1133 P2Y11 ATP?S˜BzATP>ATP Suramin>RB 2, NF157, Gq/G11 y Gs Brain, placenta, pituitary
>2MeSATP 5´-AMPs PLCß/IP3/Ca2+ gland, gut, immune system,
AC Activation granulocytes