Page 328 - 73_04
P. 328
M.ª TERESA MIRAS-PORTUGAL Y COLS. ANAL. REAL ACAD. NAC. FARM.
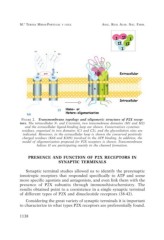
FIGURE 2. Transmembrane topology and oligomeric structure of P2X recep-
tors. The intracellular N- and C-termini, two transmebrane domains (M1 and M2)
and the extracellular ligand-binding loop are shown. Conservatives cysteines
residues, organized in two domains (C1 and C2), and the glycosilation sites are
indicated. Moreover, in the extracellular loop is shown the conserved positively
charged residues (K68 and K309) involved in the ATP binding. In addition, the
model of oligomerization proposed for P2X receptors is shown. Transmembrane
helixes II are participating mainly in the channel formation.
PRESENCE AND FUNCTION OF P2X RECEPTORS IN
SYNAPTIC TERMINALS
Synaptic terminal studies allowed us to identify the presynaptic
ionotropic receptors that responded specifically to ATP and some
more specific agonists and antagonists, and even link them with the
presence of P2X subunits through immunohistochemistry. The
results obtained point to a coexistence in a single synaptic terminal
of different types of P2X and dinucleotide receptors (38-42).
Considering the great variety of synaptic terminals it is important
to characterize in what types P2X receptors are preferentially found.
1138