Page 231 - 73_04
P. 231
VOL. 73 (4), 1031-1045, 2007 EARLY NEURAL CELL DEATH: AN OVERLOOKED...
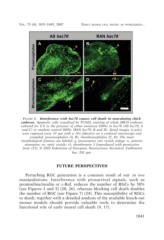
FIGURE 6. Interference with hsc70 causes cell death in neurulating chick
embryos. Apoptotic cells visualized by TUNEL staining of whole HH10 embryos
cultured for 8 h in the presence of either antisense ODNs to hsc70 (AS hsc70; A
and C) or random control ODNs (RAN hsc70; B and D). Serial images (z-axis)
were captured every 10 µm with a 10× objective on a confocal microscope and
compiled: prosencephalon (A, B), rhombencephalon (C, D). The main
morphological features are labeled: g, presumptive otic vesicle anlage; n, anterior
neuropore; ov, optic vesicle; r3, rhombomere 3 [reproduced with permission
from (23); © 2002 Federation of European Neuroscience Societies]. Calibration
bar, 200 µm.
FUTURE PERSPECTIVES
Perturbing RGC generation is a common result of our in ovo
manipulations. Interference with prosurvival signals, such as
proinsulina/insulin or c-Raf, reduces the number of RGCs by 50%
(see Figures 3 and 5) (20, 26), whereas blocking cell death doubles
the number of RGC (see Figure 7) (24). This susceptibility of RGCs
to death, together with a detailed analysis of the available knock-out
mouse models should provide valuable tools to determine the
functional role of early neural cell death (9, 17).
1041