Page 86 - 83_01
P. 86
3.2. M2 cytokines or sp2-iminosugar derivative R-DS-ONJ Ana I. Arroba, Ángela M. Valverde
decreased the pro-inflammatory signaling pathways
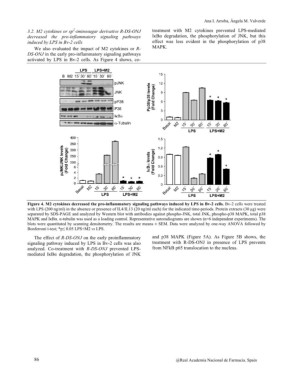
induced by LPS in Bv-2 cells treatment with M2 cytokines prevented LPS-mediated
I?Ba degradation, the phosphorylation of JNK, but this
We also evaluated the impact of M2 cytokines or R- effect was less evident in the phosphorylation of p38
DS-ONJ in the early pro-inflammatory signaling pathways MAPK.
activated by LPS in Bv-2 cells. As Figure 4 shows, co-
Figure 4. M2 cytokines decreased the pro-inflammatory signaling pathways induced by LPS in Bv-2 cells. Bv-2 cells were treated
with LPS (200 ng/ml) in the absence or presence of IL4/IL13 (20 ng/ml each) for the indicated time-periods. Protein extracts (30 µg) were
separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blot with antibodies against phospho-JNK, total JNK, phospho-p38 MAPK, total p38
MAPK and I?Ba. a-tubulin was used as a loading control. Representative autoradiograms are shown (n=6 independent experiments). The
blots were quantitated by scanning densitometry. The results are means ± SEM. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by
Bonferroni t-test; *p= 0.05 LPS+M2 vs LPS.
The effect of R-DS-ONJ on the early proinflammatory and p38 MAPK (Figure 5A). As Figure 5B shows, the
signaling pathway induced by LPS in Bv-2 cells was also treatment with R-DS-ONJ in presence of LPS prevents
analyzed. Co-treatment with R-DS-ONJ prevented LPS- from NFkB p65 translocation to the nucleus.
mediated I?Ba degradation, the phosphorylation of JNK
86 @Real Academia Nacional de Farmacia. Spain