Page 139 - Demo
P. 139
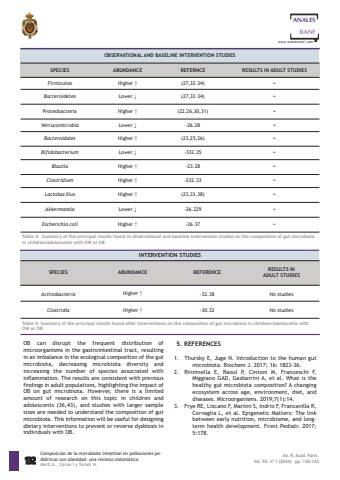
5. REFERENCES1. Thursby E, Juge N. Introduction to the human gutmicrobiota. Biochem J. 2017; 16: 1823-36. 2. Rinninella E, Raoul P, Cintoni M, Franceschi F,Miggiano GAD, Gasbarrini A, et al. what is thehealthy gut microbiota composition? A changingecosystem across age, environment, diet, anddiseases. Microorganisms. 2019;7(1):14. 3. Frye RE, Lizcano F, Martini S, Indrio F, Francavilla R,Corvaglia L, et al. Epigenetic Matters: The linkbetween early nutrition, microbiome, and longterm health development. Front Pediatr. 2017;5:178. OB can disrupt the frequent distribution ofmicroorganisms in the gastrointestinal tract, resultingin an imbalance in the ecological composition of the gutmicrobiota, decreasing microbiota diversity andincreasing the number of species associated withinflammation. The results are consistent with previousfindings in adult populations, highlighting the impact ofOB on gut microbiota. However, there is a limitedamount of research on this topic in children andadolescents (36,43), and studies with larger samplesizes are needed to understand the composition of gutmicrobiota. This information will be useful for designingdietary interventions to prevent or reverse dysbiosis inindividuals with OB.132ANALESRANFwww.analesranf.comComposici%u00f3n de la microbiota intestinal en poblaciones pedi%u00e1tricas con obesidad: una revisi%u00f3n sistem%u00e1ticaMarti A., Canas I y Tamez H.An. R. Acad. Farm.Vol. 90. n%u00ba 1 (2024) %u00b7 pp. 125-135OBSERVATIONAL AND BASELINE INTERVENTION STUDIESSPECIES ABUNDANCE REFERNCE RESULTS IN ADULT STUDIESFirmicutes Higher %u2191 (27,32%u201334) =Bacteroidetes Lower %u2193 (27,32%u201334) =Proteobacteria Higher %u2191 (22,26,30,31) =Verrucomicrobia Lower %u2193 -26.28 =Bacteroidales Higher %u2191 (23,25,26) =Bifidobacterium Lower %u2193 -332.35 =Blautia Higher %u2191 -23.28 =Clostridium Higher %u2191 -232.33 =Lactobacillus Higher %u2191 (23,33,38) =Akkermansia Lower %u2193 -26.229 =Escherichia coli Higher %u2191 -26.37 =Table 4: Summary of the principal results found in observational and baseline intervention studies on the composition of gut microbiotain children/adolescents with OW or OBTable 5: Summary of the principal results found after interventions on the composition of gut microbiota in children/adolescents withOW or OBINTERVENTION STUDIESSPECIES ABUNDANCE REFERENCE RESULTS IN ADULT STUDIESActinobacteria Higher %u2191 -32.38 No studies Clostridia Higher %u2191 -30.32 No studies