Page 20 - 82_01
P. 20
Coronary ischemia-reperfusion: role of nitric oxide and endothelin-1. A Review
as a consequence of the reaction of NO with hemoglobin. three forms of NO synthase (endothelial NO (eNO)
synthase, neuronal NO (nNO) synthase, and inducible
This molecule can become highly toxic to tissues NO (iNO) synthase). The brain proved to be a rich source
during some pathological conditions (e. g., ischemia and of NO synthesis and allowed the first NO synthase to be
reperfusion). NO by reacting with anion superoxide cloned and purified (45, 46). It is called nNOS or NOS1
(O2•-) forms peroxynitrite (ONOO-), which is a as it was the first synthase to be cloned. The NOS1 gene
powerful oxidant and seems to be a determinant in the has the most complex genomic organization in humans
contrasting roles of NO in physiology and pathology. with multiple splice variants being produced (47). The
Peroxynitrite interacts with lipids, DNA, and proteins via second NO synthase to be cloned was isolated from
direct oxidative reactions or via indirect, radical- macrophages and is known as NOS2 or iNOS (inducible
mediated mechanisms, which may commit cells to NOS) because it is readily induced in many tissues by
necrosis or apoptosis. In vivo, peroxynitrite generation proinflammatory cytokines. Because NOS2 can be
represents a crucial pathogenic mechanism in conditions strongly induced by proinflammatory stimuli, it induces
such as stroke, myocardial infarction, chronic heart often a high production of NO. The first source of NO
failure, diabetes mellitus, circulatory shock, chronic identified was the endothelium, but eNO synthase was
inflammatory diseases, cancer, and neurodegenerative the last to be cloned and is known as eNOS or NOS3.
disorders. NOS3 binds to plasma membranes and is typically
associated with caveolin (48). It is strongly activated by
The regulation and synthesis of NO by mammalian the entry of calcium through membrane-bound receptors
cells has been the focus of many reviews (36, 37), as and is also regulated by phosphorylation (49). NOS3 is
have been many of its physiological and pathological also found in neurons and other tissues in addition to
actions (38, 39). For a century, nitrovasodilators had been endothelium (36). NO is also produced by myocardium,
used clinically without understanding their mechanism of and it is involved in several aspects of physiological
action. Alfred Nobel lamented the irony that he was myocardial function (e. g., excitation-contraction
taking nitroglycerin to treat angina after making his coupling; myocardial relaxation; diastolic function; the
fortune developing dynamite. Frank-Starling response; heart rate; ß-adrenergic
inotropic response; and myocardial energetics and
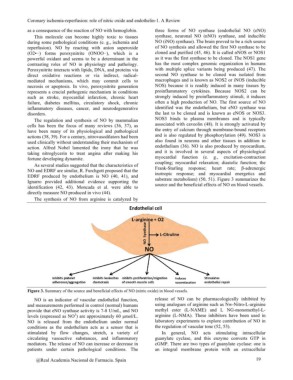
As several studies suggested that the characteristics of substrate metabolism) (50, 51). Figure 3 summarizes the
NO and EDRF are similar, R. Furchgott proposed that the source and the beneficial effects of NO on blood vessels.
EDRF produced by endothelium is NO (40, 41), and
Ignarro provided additional evidence supporting the
identification (42, 43). Moncada et al. were able to
directly measure NO produced in vivo (44).
The synthesis of NO from arginine is catalyzed by
Figure 3. Summary of the source and beneficial effects of NO (nitric oxide) in blood vessels.
NO is an indicator of vascular endothelial function, release of NO can be pharmacologically inhibited by
and measurements performed in control (normal) humans using analogues of arginine such as Nw-Nitro-L-arginine
provide that eNO synthase activity is 7-8 U/mL, and NO methyl ester (L-NAME) and L NG-monomethyl-L-
levels (expressed as NO3) are approximately 60 µmol/L. arginine (L-NMA). These inhibitors have been used in
NO is released from the endothelium under normal laboratory experiments to explore contribution of NO in
conditions as the endothelium acts as a sensor that is the regulation of vascular tone (52, 53).
stimulated by flow changes, stretch, a variety of
circulating vasoactive substances, and inflammatory In general, NO acts stimulating intracellular
mediators. The release of NO can increase or decrease in guanylate cyclase, and this enzyme converts GTP in
patients under certain pathological conditions. The cGMP. There are two types of guanylate cyclase: one is
an integral membrane protein with an extracellular
@Real Academia Nacional de Farmacia. Spain 19