Page 25 - 82_01
P. 25
ET-1 may also exert other vascular functions, as for Godofredo Diéguez Castrillo
example to modulate the response of coronary arteries to
other types of vasoactive stimuli. The relaxation to increased the contraction to AVP in ear (148% of
isoproterenol, field electrical stimulation, Ach, and control), basilar (150% of control), renal (304% of
sodium nitroprusside was recorded in isolated coronary control), coronary (437% of control) and saphenous
arteries from rats, in the absence and in the presence of (235% of control) arteries. Removal of the endothelium
ET-1. It was found that the treatment with ET-1 increased increased the contraction to AVP in basilar (138% of
the relaxation to isoproterenol and did not modify the control), renal (253% of control), coronary (637% of
relaxation to electrical stimulation, Ach, or sodium control) and saphenous (662% of control) arteries, but
nitroprusside The increased relaxation to isoproterenol in not in ear artery. Mesenteric and pulmonary arteries in
the presence of ET-1 was also present in the presence of the presence of L-NAME or after endothelium removal
the endothelin ETB antagonist BQ788 but disappeared in did not respond to AVP, as occurred in control
the presence of the endothelin ETA antagonist BQ123 or conditions. The specific blockade of V1 vasopressin
the blocker of protein kinase C chelerythrine. Thus, receptors was more potent than the blockade of both V1
curiously, ET-1 may potentiate coronary beta-adrenergic and V2 vasopressin receptors to block the contraction to
vasodilatation, due at least in part to stimulation of AVP. In arteries precontracted with endothelin-1,
endothelin ETA receptors and activation of protein vasopressin or desmopressin did not produce relaxation.
kinase C (97). Therefore, these results suggest: a) most arterial beds
studied (5 of 7) exhibit contraction to AVP with different
Arginine-vasopressin (AVP) is a hormone that may intensity; b) the vasoconstriction to this peptide is
be of significance in the regulation of coronary mediated mainly by stimulation of V1 vasopressin
circulation, particularly under certain pathological receptors, and c) endothelial NO may inhibit the
conditions such as myocardial infartion (see below vasoconstriction to this peptide, especially in coronary
Ischemia-reperfusion). In anesthetized goats we have and renal vasculatures (99). From this study (99) it is
found that under normal conditions, AVP produces apparent that NO plays a relevant role in modulating the
coronary vasoconstriction and that this vasoconstriction vascular effects of AVP, and that this role is relatively
may be mediated by vasopressin V1 receptors, without more pronounced in coronary vasculature than in other
involvement of vasopressin V2 receptors; and it is vasculatures. In other study we compared the coronary
probably modulated by NO, but not by prostanoids (98). effects of ET-1 and AVP in anesthetized goats, and the
These results in coronary vasculature of goats are in line results suggest that ET-1 is more effective than AVP for
with those obtained in coronary vasculature from rabbits producing coronary vasoconstriction (Figure 7), that NO
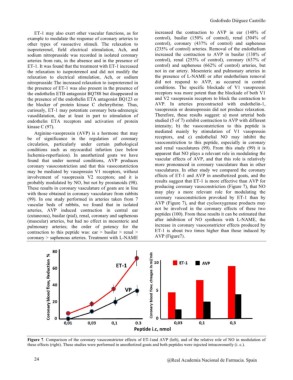
(99). In one study performed in arteries taken from 7 may play a more relevant role for modulating the
vascular beds of rabbits, we found that in isolated coronary vasoconstriction provoked by ET-1 than by
arteries, AVP induced contraction in central ear AVP (Figure 7), and that cyclooxygenase products may
(cutaneous), basilar (pial), renal, coronary and saphenous not be involved in the coronary effects of these two
(muscular) arteries, but had no effect in mesenteric and peptides (100). From these results it can be estimated that
pulmonary arteries; the order of potency for the after inhibition of NO synthesis with L-NAME, the
contraction to this peptide was: ear > basilar > renal > increase in coronary vasoconstrictor effects produced by
coronary > saphenous arteries. Treatment with L-NAME ET-1 is about two times higher than those induced by
AVP (Figure7).
Figure 7. Comparison of the coronary vasoconstrictor effects of ET-1and AVP (left), and of the relative role of NO in modulation of
these effects (right). These studies were performed in anesthetized goats and both peptides were injected intracoronarily (i. c.).
24 @Real Academia Nacional de Farmacia. Spain