Page 17 - 82_01
P. 17
management of patients with ischemic heart disease. The Godofredo Diéguez Castrillo
basic understanding of the flow mechanics of coronary
stenoses have been also translated to the cardiac metabolism, neural factors, circulating vasoactive
catherization laboratory where measurements of coronary substances, and endothelial factors (1, 17, 18).
pressure distal to a stenosis and coronary blood flow are Myocardial function is closely coupled to coronary blood
routinely obtained (15, 16). flow and oxygen delivery, thus balance between oxygen
supply and myocardial demand is a critical determinant
The coronary circulation provides oxygen and of the normal heart function (1, 17-19). Figure 1shows a
nutrients to heart tissue, and the myocardium is very schematic representation of different aspects of the
sensitive to oxygen deprivation. Coronary blood flow is human coronary circulation.
determined, essentially, by aortic pressure, myocardial
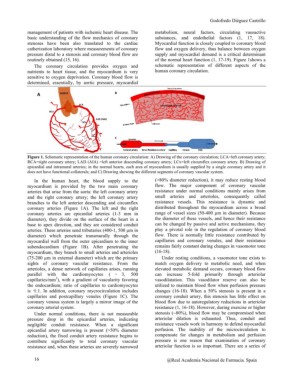
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the human coronary circulation: A) Drawing of the coronary circulation; LCA=left coronary artery;
RCA=right coronary artery; LAD (AIA) =left anterior descending coronary artery; LCx=left circumflex coronary artery. B) Drawing of
epicardial and intramural arteries; in the normal hearts, each area of myocardium is usually supplied by a single coronary artery and it
does not have functional collaterals; and C) Drawing showing the different segments of coronary vascular system.
In the human heart, the blood supply to the (>80% diameter reduction), it may reduce resting blood
myocardium is provided by the two main coronary flow. The major component of coronary vascular
arteries that arise from the aorta: the left coronary artery resistance under normal conditions mainly arises from
and the right coronary artery; the left coronary artery small arteries and arterioles, consequently called
branches to the left anterior descending and circumflex resistance vessels. This resistance is dynamic and
coronary arteries (Figure 1A). The left and the right distributed throughout the myocardium across a broad
coronary arteries are epicardial arteries (1-3 mm in range of vessel sizes (50-400 µm in diameter). Because
diameter), they divide on the surface of the heart in a the diameter of these vessels, and hence their resistance
base to apex direction, and they are considered conduit can be changed by passive and active mechanisms, they
arteries. These arteries send tributaries (400-1, 500 µm in play a pivotal role in the regulation of coronary blood
diameter) which penetrate transmurally through the flow. There is normally little resistance contributed by
myocardial wall from the outer epicardium to the inner capillaries and coronary venules, and their resistance
subendocardium (Figure 1B). After penetrating the remains fairly constant during changes in vasomotor tone
myocardium, they branch to small arteries and arterioles (16-18).
(75-200 µm in external diameter) which are the primary
sights of coronary vascular resistance. From the Under resting conditions, a vasomotor tone exists to
arterioles, a dense network of capillaries arises, running match oxygen delivery to metabolic need, and when
parallel with the cardiomyocytes ( ? 3, 500 elevated metabolic demand occurs, coronary blood flow
capillaries/mm2), with a gradient of vascularity favoring can increase 5-fold primarily through arteriolar
the endocardium; ratio of capillaries to cardiomyocytes vasodilatation. This vasodilator reserve can also be
is ?1:1. In addition, coronary mycrocirculation includes utilized to maintain blood flow when perfusion pressure
capillaries and postcapillary venules (Figure 1C). The changes (16-18). When a 50% stenosis is present in a
coronary venous system is largely a mirror image of the coronary conduit artery, this stenosis has little effect on
coronary arterial system. blood flow due to autoregulatory reductions in arteriolar
resistance (1, 16-18). However, during exercise or higher
Under normal conditions, there is not measurable stenosis (~80%), blood flow may be compromised when
pressure drop in the epicardial arteries, indicating arteriolar dilation is exhausted. Thus, conduit and
negligible conduit resistance. When a significant resistance vessels work in harmony to defend myocardial
epicardial artery narrowing is present (>50% diameter perfusion. The inability of the microcirculation to
reduction), the fixed conduit artery resistance begins to compensate for changes in metabolism and perfusion
contribute significantly to total coronary vascular pressure is one reason that examination of coronary
resistance and, when these arteries are severely narrowed arteriolar function is so important. There are a series of
16 @Real Academia Nacional de Farmacia. Spain