Page 56 - 81_02
P. 56
maturation into active oxidases. In NOX-1/NOX-3 Andrea Aguado et al.
systems, p22phox also promotes plasma membrane and ROS production is regulated by Poldip2 (Figure 7).
targeting of the oxidases and provides a docking site for NOX-5 and DUOX are Ca2+-responsive oxidases that
NOX organizers. However, NOX-4 only depends on contain Ca2+-binding domain (Figure 7). NOX-1, NOX-2,
p22phox in order to be active, is constitutively activated, NOX-3 and NOX-5 produce O2•- while NOX-4, DUOX-1
and DUOX-2 produce H2O2 (34, 55).
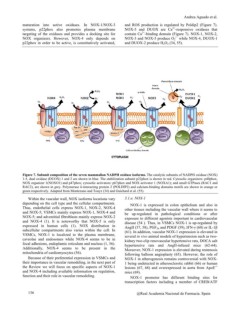
Figure 7. Subunit composition of the seven mammalian NADPH oxidase isoforms. The catalytic subunits of NADPH oxidase (NOX)
1-5, dual oxidase (DUOX) 1 and 2 are shown in blue. The stabilization subunit p22phox is shown in red. Cytosolic organizers: p40phox,
NOX organizer 1(NOXO1) and p47phox; cytosolic activators: p67phox and NOX activator 1 (NOXA1); and small GTPases (RAC1 and
RAC2), are shown in grey. Polymerase d-interacting protein 2 (POLDIP2) and calcium-binding domains motifs are shown in orange or
green respectively. Adapted from Montezano and Touyz (34) and Guichard et al. (55).
Within the vascular wall, NOX isoforms locations vary 3.1.a. NOX-1
depending on the cell type and the cellular compartments.
Thus, endothelial cells express NOX-1, NOX-2, NOX-4 NOX-1 is expressed in colon epithelium and also in
and NOX-5; VSMCs mainly express NOX-1, NOX-4 and other tissues including the vascular wall where it seems to
NOX-5; and adventitial fibroblasts mainly express NOX-2 be up-regulated in pathological conditions or after
and NOX-4 (1). It is noteworthy that NOX-5 is only exposure to different agonists important in cardiovascular
expressed in human cells (1). NOX distribution in disease (54 ). Thus, in VSMCs NOX-1 is up-regulated by
subcellular compartments also varies within the cell. In AngII (57, 58), PGF2a and PDGF (59), IFN-? (60) or IL-1ß
VSMCs, NOX-1 is localized to the plasma membrane, (61). In addition, vascular NOX-1 expression is elevated in
caveolae and endosomes while NOX-4 seems to be in several in vivo animal models of hypertension such as two-
focal adhesions, endoplamic reticulum and nucleus (1, 56). kidney two-clip renovascular hypertensive rats, DOCA salt
Additionally, NOX-4 seems to be present in the hypertensive rats and AngII-infused mice (62-64).
mitochondria of cardiomyocytes (56). Moreover, NOX-1 expression is elevated during restenosis
following balloon angioplasty (65). However, the role of
Because of their preferential expression in VSMCs and NOX-1 in atherogenesis remains controversial with NOX-
their importance in vascular remodeling, in the next part of 1 being undetected in atherosclerotic rabbit (66) or human
the Review we will focus on specific aspects of NOX-1 lesions (67, 68) and overexpressed in aorta from ApoE-/-
and NOX-4 including available information on regulation, mice (69).
function and their role in vascular remodeling.
NOX-1 promoter has different binding sites for
transcription factors including a member of CREB/ATF
136 @Real Academia Nacional de Farmacia. Spain