Page 79 - 76_03
P. 79
VOL. 76 (3), 357-377, 2010 TSC1-TSC2 COMPLEX ON THE CROSSROAD OF PANCREATIC...
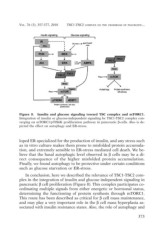
Figure 8. Insulin and glucose signaling toward TSC complex and mTORC1.
Integration of insulin or glucose-independent signaling by TSC1-TSC2 complex con-
verging on mTORC1/p70S6K proliferation pathway in pancreatic ß-cells. Also is de-
picted the effect on autophagy and ER-stress.
loped ER specialized for the production of insulin, and any stress such
as in vitro culture makes them prone to misfolded protein accumula-
tion, and extremely sensible to ER-stress mediated cell death. We be-
lieve that the basal autophagic level observed in ß cells may be a di-
rect consequence of the higher misfolded protein accumulation.
Finally, we found autophagy to be protective under certain conditions
such as glucose starvation or ER-stress.
In conclusion, here we described the relevance of TSC1-TSC2 com-
plex in the integration of insulin and glucose independent signaling in
pancreatic ß cell proliferation (Figure 8). This complex participates co-
ordinating multiple signals from either energetic or hormonal status,
determining the functioning of protein synthesis through mTORC1.
This route has been described as critical for ß cell mass maintenance,
and may play a very important role in the ß cell mass hyperplasia as-
sociated with insulin resistance states. Also, the role of autophagy and
373