Page 120 - 82_02
P. 120
catalytic subunits, MATa1 and MATa2, and the María Ángeles Pajares
regulatory subunit MATß, respectively (Figure 2). The
high level of identity exhibited by MATa1 and MATa2 oxidoreductase family (4,5). Four splicing forms of MATß
(85% at the amino acid level), is not shared by MATß, have been detected in hepatoma cells, from which the V1
which is a non-related protein of the PFAM 04321 form is the protein encountered in normal tissues and
which has been evaluated in most studies published to date
(51).
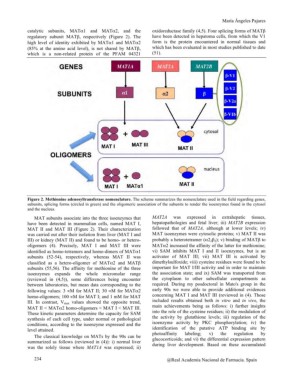
Figure 2. Methionine adenosyltransferase nomenclature. The scheme summarizes the nomenclature used in the field regarding genes,
subunits, splicing forms (circled in green) and the oligomeric association of the subunits to render the isoenzymes found in the cytosol
and the nucleus.
MAT subunits associate into the three isoenzymes that MAT2A was expressed in extrahepatic tissues,
have been detected in mammalian cells, named MAT I, hepatopathologies and fetal liver; iii) MAT2B expression
MAT II and MAT III (Figure 2). Their characterization followed that of MAT2A, although at lower levels; iv)
was carried out after their isolation from liver (MAT I and MAT isoenzymes were cytosolic proteins; v) MAT II was
III) or kidney (MAT II) and found to be homo- or hetero-
oligomers (4). Precisely, MAT I and MAT III were probably a heterotetramer (a22ß2); v) binding of MATß to
MATa2 increased the affinity of the latter for methionine;
identified as homo-tetramers and homo-dimers of MATa1 vi) SAM inhibits MAT I and II isoenzymes, but is an
subunits (52-54), respectively, whereas MAT II was activator of MAT III; vii) MAT III is activated by
dimethylsulfoxide; viii) cysteine residues were found to be
classified as a hetero-oligomer of MATa2 and MATß important for MAT I/III activity and in order to maintain
subunits (55,56). The affinity for methionine of the three the association state; and ix) SAM was transported from
isoenzymes expands the whole micromolar range the cytoplasm to other subcellular compartments as
(reviewed in (4,5)), some differences being encounter required. During my posdoctoral in Mato's group in the
between laboratories, but mean data corresponding to the early 90s we were able to provide additional evidences
following values: 3 µM for MAT II; 30 µM for MATa2 concerning MAT I and MAT III (reviewed in (4). Those
homo-oligomers; 100 µM for MAT I; and 1 mM for MAT included results obtained both in vitro and in vivo, the
III. In contrast, Vmax values showed the opposite trend, main achievements being as follows: i) further insights
MAT II < MATa2 homo-oligomers < MAT I < MAT III. into the role of the cysteine residues; ii) the modulation of
These kinetic parameters determine the capacity for SAM the activity by glutathione levels; iii) regulation of the
synthesis of each cell type, under normal or pathological isoenzyme activity by PKC phosphorylation; iv) the
conditions, according to the isoenzyme expressed and the identification of the putative ATP binding site by
level attained. photoaffinity labeling; v) the regulation by
glucocorticoids; and vi) the differential expression pattern
The classical knowledge on MATs by the 90s can be during liver development. Based on these accumulated
summarized as follows (reviewed in (4)): i) normal liver
was the solely tissue where MAT1A was expressed; ii)
234 @Real Academia Nacional de Farmacia. Spain