Page 29 - 82_01
P. 29
thus represents a target for cardioprotection. At present, Godofredo Diéguez Castrillo
no effective therapy exists for this situation. It has been
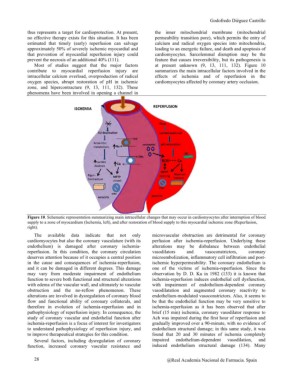
estimated that timely (early) reperfusion can salvage the inner mitochondrial membrane (mitochondrial
approximately 50% of severely ischemic myocardial and permeability transition pore), which permits the entry of
that prevention of myocardial reperfusion injury could calcium and radical oxygen species into mitochondria,
prevent the necrosis of an additional 40% (111). leading to an energetic failure, and death and apoptosis of
cardiomyocytes. Sarcolemmal disruption may be the
Most of studies suggest that the major factors feature that causes irreversibility, but its pathogenesis is
contribute to myocardial reperfusion injury are at present unknown (9, 13, 111, 132). Figure 10
intracellular calcium overload, overproduction of radical summarizes the main intracellular factors involved in the
oxygen species, abrupt restoration of pH in ischemic effects of ischemia and of reperfusion in the
zone, and hipercontracture (9, 13, 111, 132). These cardiomyocytes affected by coronary artery occlusion.
phenomena have been involved in opening a channel in
Figure 10. Schematic representation summarizing main intracellular changes that may occur in cardiomyocytes after interruption of blood
supply to a zone of myocardium (Ischemia, left), and after restoration of blood supply to this myocardial ischemic zone (Reperfusion,
right).
The available data indicate that not only microvascular obstruction are detrimental for coronary
cardiomyocytes but also the coronary vasculature (with its perfusion after ischemia-reperfusion. Underlying these
endothelium) is damaged after coronary ischemia- alterations may be disbalance between endothelial
reperfusion. In this condition, the coronary circulation vasodilators and vasoconstrictors, coronary
deserves attention because of it occupies a central position microembolization, inflammatory cell infiltration and post-
in the cause and consequences of ischemia-reperfusion, ischemic hyperpermeability. The coronary endothelium is
and it can be damaged in different degrees. This damage one of the victims of ischemia-reperfusion. Since the
may vary from moderate impairment of endothelium observation by D. D. Ku in 1982 (133) it is known that
function to severe both functional and structural alterations ischemia-reperfusion induces endothelial cell dysfunction,
with edema of the vascular wall, and ultimately to vascular with impairment of endothelium-dependent coronary
obstruction and the no-reflow phenomenon. These vasodilatation and augmented coronary reactivity to
alterations are involved in dysregulation of coronary blood endothelium-modulated vasoconstrictors. Also, it seems to
flow and functional ability of coronary collaterals, and be that the endothelial function may be very sensitive to
therefore in evolution of ischemia-reperfusion and in ischemia-reperfusion as it has been observed that after
pathophysiology of reperfusion injury. In consequence, the brief (15 min) ischemia, coronary vasodilator response to
study of coronary vascular and endothelial function after Ach was impaired during the first hour of reperfusion and
ischemia-reperfusion is a focus of interest for investigators gradually improved over a 90-minute, with no evidence of
to understand pathophysiology of reperfusion injury, and endothelium structural damage; in this same study, it was
to improve therapeutical strategies for this condition. found that 20 and 30 minutes of ischemia completely
impaired endothelium-dependent vasodilation, and
Several factors, including dysregulation of coronary induced endothelium structural damage (134). Many
function, increased coronary vascular resistance and
28 @Real Academia Nacional de Farmacia. Spain