Page 6 - 72_04
P. 6
ISABEL LÓPEZ DE SILANES Y MANEL ESTELLER AN. R. ACAD. NAC. FARM.
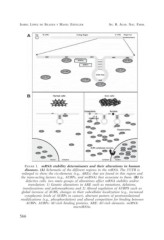
FIGURE 1. mRNA stability determinants and their alterations in human
diseases. (A) Schematic of the different regions in the mRNA. The 3’UTR is
enlarged to show the cis-elements (e.g., AREs) that are found in this region and
the trans-acting factors (e.g., AUBPs, and miRNA) that associate to them. (B) In
defective cells, two main groups of alterations affect mRNA stability and/or
translation: 1) Genetic alterations in ARE such as mutations, deletions,
translocations and polymorphisms and 2) Altered regulation of AUBPS such as
global increase of AUBS, changes in their subcellular localization (e.g., increased
cytoplasmic levels of AUBPs in cancer), aberrant pattern of posttranslational
modifications (e.g., phosphorylation) and altered competition for binding between
AUBPs. AUBPs: AU-rich binding proteins. ARE: AU-rich elements. miRNA:
microRNAs.
566