Page 87 - 81_02
P. 87
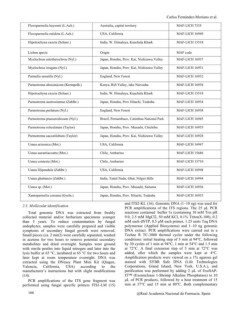
Flavoparmelia haysonii (L.Ach.) Australia, capital territory Carlos Fernández-Moriano et al.
Flavoparmelia rutidota (L.Ach.) USA, California MAF-LICH 7535
Hipotrachyna execta (Schaer.) India, W. Himalaya, Kuachula Khark MAF-LICH 16949
MAF-LICH 15518
Lichen specie Origin MAF code
Myelochroa entotheiochroa (Nyl.) Japan, Honshu, Prov. Kai, Nishizawa Valley MAF-LICH 16937
Myelochroa irrugans (Nyl.) Japan, Honshu, Prov. Kai, Nishizawa Valley MAF-LICH 16931
Parmelia saxatilis (Nyl.) England, New Forest MAF-LICH 16932
Parmotrema abessinicum (Krempelh.) Kenya, Rift Valley, lake Naivasha MAF-LICH 16938
Hipotrachyna execta (Schaer.) India, W. Himalaya, Kuachula Khark MAF-LICH 15518
Parmotrema austrosinense (Zahlbr.) Japan, Honshu, Prov Hitachi, Tsukuba MAF-LICH 16934
Parmotrema perlatum (Nyl.) England, New Forest MAF-LICH 16938
Parmotrema praeserediosum (Nyl.) Brazil, Pernambuco, Catimbau National Park MAF-LICH 16945
Parmotrema reticulatum (Taylor) Japan, Honshu, Prov. Musashi, Chichibu MAF-LICH 16935
Parmotrema saccatilobum (Taylor) Japan, Honshu, Prov. Kai, Nishizawa Valley MAF-LICH 16928
Usnea arizonica (Mot.) USA, California MAF-LICH 16947
Usnea aurantiacoatra (Mot.) Chile, Ambarino MAF-LICH 15686
Usnea contexta (Mot.) Chile, Ambarino MAF-LICH 15710
Usnea filipendula (Zahlbr.) USA, California MAF-LICH 16948
Usnea ghattensis (Zahlbr.) India, Tamil Nadu, Ghat, Nilgiri Hills MAF-LICH 16944
Usnea sp. (Mot.) Japan, Honshu, Prov. Musashi, Saitama MAF-LICH 16936
Xantoparmelia coreana (Gyeln.) Japan, Honshu, Prov. Hitachi, Tsukuba MAF-LICH 16933
2.3. Mollecular identification and ITS2-KL (16). Genomic DNA (1–10 ng) was used for
PCR amplifications of the ITS regions. The 25 µL PCR
Total genomic DNA was extracted from freshly reactions contained buffer 1x (containing 10 mM Tris pH
collected material and/or herbarium specimens younger 9.0, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 50 mM KCl, 0.1% TritonX-100), 0.2
than 5 years. To reduce contamination by fungal mM each dNTP, 0.5 µM each primer, 1.25 units Taq DNA
endophytes, samples were carefully prepared and visible polymerase (Applied Biosystems) and 1–10 ng genomic
symptoms of secondary fungal growth were removed. DNA extract. PCR amplifications were carried out in a
Small pieces (ca. 2 mm2) were carefully separated, washed Techne R TC-3000 thermal cycler under the following
in acetone for two hours to remove potential secondary conditions: initial heating step of 5 min at 94°C, followed
metabolites and dried overnight. Samples were ground by 30 cycles of 1 min at 94°C, 1 min at 54°C and 1.5 min
with sterile pestles into liquid nitrogen and later into the at 72°C. A final extension step of 5 min at 72°C was
lysis buffer at 65 °C, incubated at 65 °C for two hours and added, after which the samples were kept at 4°C.
later kept at room temperature overnight. DNA was Amplification products were viewed on a 1% agarose gel
extracted using the DNeasy Plant Mini Kit (Qiagen, stained with SYBR Safe DNA (Life Technologies
Valencia, California, USA) according to the Corporations, Grand Island, New York, U.S.A.), and
manufacturer’s instructions but with slight modifications purification was performed by adding 2 µL of ExoSAP-
(14). IT™ (Exonuclease 1-Shrimp Alkaline Phosphatase) to 10
µL of PCR products, followed by a heat treatment of 15
PCR amplifications of the ITS gene fragment was min at 37°C and 15 min at 80°C. Both complementary
performed using fungal specific primers ITS1-LM (15)
@Real Academia Nacional de Farmacia. Spain
166