Page 38 - 80_04
P. 38
Protein tyrosine phosphatase deficiency…
Figure 7A, APAP markedly increased the levels of phosphorylated JNK in wild-type
hepatocytes. Interestingly, the lack of PTP1B prevented JNK activation in response
to APAP.
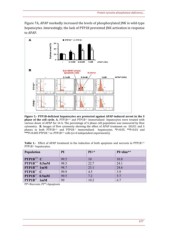
Figure 5.- PTP1B-deficient hepatocytes are protected against APAP-induced arrest in the S
phase of the cell cycle. A. PTP1B+/+ and PTP1B-/- immortalized hepatocytes were treated with
various doses of APAP for 16 h. The percentage of S phase cell population was measured by flow
cytometry. B. Images of flow cytomerty showing the effect of APAP treatment on G0/G1 and S
phases in both PTP1B+/+ and PTP1B-/- immortalized hepatocytes. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and
***P<0.005 PTP1B-/- vs. PTP1B+/+ cells (n=4 independent experiments).
Table 1.- Effect of APAP treatment in the induction of both apoptosis and necrosis in PTP1B+/+
PTP1B-/- hepatocytes.
Population PI PI+* PI+dim**
PTP1B+/+ C 99.5 10 10.8
22.7 24.1
PTP1B+/+ 0.5mM 98.5 23.1 24.6
4.5 3.9
PTP1B+/+ 1mM 98.7 7.2 5.7
10.2 6.7
PTP1B-/- C 99.9
PTP1B-/- 0.5mM 99.5
PTP1B-/- 1mM 99
PI*=Necrosis. PI**=Apoptosis
677