Page 339 - 73_04
P. 339
VOL. 73 (4), 1127-1157, 2007 PHYSIOLOGICAL ROLE OF EXTRACELLULAR...
P2Y functional responses in astrocytes
Calcium responses measured using fura-2 microfluorimetric
techniques suggest that different P2Y subtypes could be responsible
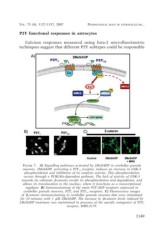
FIGURE 7. A) Signalling pathways activated by 2MeSADP in cerebellar granule
neurons. 2MeSADP, activating a P2Y13 receptor, induces an increase in GSK-3
phosphorylation and inhibition of its catalytic activity. This phosphorylation
occurs through a PI3K/Akt-dependent pathway. The lack of activity of GSK-3
towards its substrate ß-catenin avoids its phosphorylation and degradation, and
allows its translocation to the nucleus, where it functions as a transcriptional
regulator. B) Immunostainnig of the main P2Y-ADP receptors expressed in
cerebellar granule neurons, P2Y1 and P2Y13 receptors. C) Fluorescence images
of ß-catenin immunostaining in cerebellar granule neurons that were stimulated
for 10 minutes with 1 µM 2MeSADP. The increase in ß-catenin levels induced by
2MeSADP treatment was maintained in presence of the specific antagonist of P2Y1
receptor, MRS-2179.
1149