Page 180 - 73_04
P. 180
MARGARITA LORENZO Y COLS. ANAL. REAL ACAD. NAC. FARM.
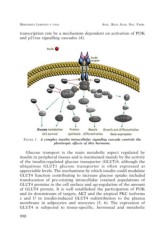
transcription rate by a mechanism dependent on activation of PI3K
and p21ras signalling cascades (4).
FIGURE 1. A complex insulin intracellular signaling cascade controls the
pleoitropic effects of this hormone.
Glucose transport is the main metabolic aspect regulated by
insulin in peripheral tissues and is maintained mainly by the activity
of the insulin-regulated glucose transporter (GLUT)4, although the
ubiquitous GLUT1 glucose transporter is often expressed at
appreciable levels. The mechanisms by which insulin could modulate
GLUT4 function contributing to increase glucose uptake included
translocation of pre-existing intracellular retained populations of
GLUT4 proteins to the cell surface and up-regulation of the amount
of GLUT4 protein. It is well established the participation of PI3K
and its downstream of targets, AKT and the atypical PKC isoforms
z and l? in insulin-induced GLUT4 redistribution to the plasma
membrane in adipocytes and myocytes (5, 6). The expression of
GLUT4 is subjected to tissue-specific, hormonal and metabolic
990