Page 144 - 73_04
P. 144
TERESA PELÁEZ Y COLS. ANAL. REAL ACAD. NAC. FARM.
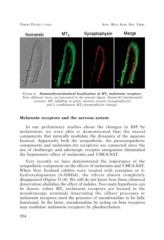
FIGURE 4. Immunohystochemical localization of MT2 melatonin receptors.
Four different views are presented in the present figure, Nomarski interferential
contrast, MT2 labelling in green, nervous system (synaptophysin)
and a combination MT2/synaptophysin (merge).
Melatonin receptors and the nervous system
In our preliminary studies about the changes in IOP by
melatonins, we were able to demonstrated that the neural
components that naturally modulate the dynamics of the aqueous
humour. Apparently both the sympathetic, the parasympathetic
components and melatonin (its receptors) are connected since the
use of cholinergic and adrenergic receptor antagonists diminished
the hypotensive effect of melatonin and 5-MCA-NAT.
Very recently we have demonstrated the importance of the
sympathetic component on the effects of melatonin and 5-MCA-NAT.
When New Zealand rabbits were treated with reserpine or 6-
hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA), the effects almost completely
disappeared (Figure 5) (8). We still do not know how these chemical
denervation abolishes the effect of indoles. Two main hypothesis can
be drawn, either MT3 melatonin receptors are located in the
noradrenergic terminals innervating the cilliary processes or
melatonin receptors need the presence of noradrenaline to be fully
functional. In the latter, noradrenaline by acting on beta receptors
may modulate melatonin receptors by phosharylation.
954