Page 154 - 71_04
P. 154
LAURA TEIXIDÓ Y COLS. AN. R. ACAD. NAC. FARM.
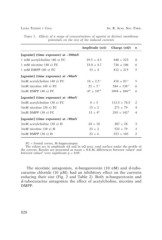
TABLE 1. Effects of a range of concentrations of agonist at distinct membrane
potentials on the size of the induced currents
Amplitude (nA) Charge (nQ) n
[agonist] (time exposure) at –100mV 29.5 ± 4.5 440 ± 223 8
1 mM acetylcholine (40 s) FC 33.8 ± 4.7 736 ± 106 6
1 mM nicotine (40 s) FC 812 ± 215 5
1 mM DMPP (40 s) FC 33 ± 4
418 ± 83 a 5
[agonist] (time exposure) at –90mV 18 ± 2.5 a 584 ± 138 a 6
3mM acetylcholine (40 s) FC 25 ± 5 a 1094 ± 206a,b 6
3mM nicotine (40 s) FC 47 ± 10a,b
3mM DMPP (40 s) FC 113.5 ± 78.5 2
8±5 271 ± 79 4
[agonist] (time exposure) at –80mV 15 ± 2 4
3mM acetylcholine (30 s) FC 15 ± 4b 295 ± 142,b
3mM nicotine (30 s) FC
3mM DMPP (30 s) FC 24 ± 10 207 ± 28 3
23 ± 2 522 ± 79 3
[agonist] (time exposure) at –90mV 22 ± 6 253 ± 103 2
3mM acetylcholine (30 s) H
3mM nicotine (30 s) H
3mM DMPP (30 s) H
FC = frontal cortex, H=hippocampus.
The values are in amplitude nA and in nQ area, total surface under the profile of
the current. Results are presented as mean ± S.E.M, differences between valuesa and
between valuesb were significant p < 0.05.
The nicotinic antagonists, a-bungarotoxin (10 nM) and d-tubo-
curarine chloride (10 µM), had an inhibitory effect on the currents
reducing their size (Fig. 2 and Table 2). Both a-bungarotoxin and
d-tubocurarine antagonize the effect of acetylcholine, nicotine and
DMPP.
828