Page 60 - 83_01
P. 60
Mitochondrial ROS and mtDNA fragments inside nuclear DNA as a main effector of ageing: the “cell aging regulation system”
subunits leading to increases in mtROS generation. Since changes in the expression of a large number of genes and
it is known that GSSG thiolization of isolated complex I proteins involved in lipid metabolism (78). In addition,
increases its rate of ROS production (108) a similar modifications of DNA methylation could be also involved
reaction of methanethiol, or cysteine (which also has a free (109, 110). Methionine is an essential amino acid with
thiol group available for direct reaction) with complex I many key roles in mammalian metabolism including
thiol groups could be involved in the decrease in mitROSp protein synthesis and function, as well as protein and DNA
in MetR. Methionine restriction decreases hepatic methylation (111). Since ageing seems to be associated
methionine and cysteine (78) and likely methanetiol levels, with site-specific changes in DNA methylation (112-116),
which can decrease thiolization of complex I subunits and MetR diets could also extend longevity in rodents through
then their rates of mitROSp. Alternatively, cysteine could modulation of DNA methylation patterns, specific changes
also interact with the protein cysteines of some of the FeS in gene expression, and changes in translation rates, whose
clusters of the hydrophilic matrix domain of complex I. final effects could include decreases in mtROS generation
Interestingly, those FeS clusters have been pointed out as and oxidative damage and increases in autophagy (see
the ROS generator relevant for aging (15,18,47). Their section 9). In agreement with that, we have recently
reaction with cysteine would lead to iron release or detected that MetR induces a small but statistically
availability for reaction and then to ROS generation. signi?cant decrease in global genomic DNA methylation in
Therefore, the lowered cysteine levels in MetR could also the heart of young immature rats (98), whereas when this
manipulation was performed in old rats the decrease in this
decrease mitROSp through this kind of mechanism.
parameter was not statistically signi?cant in the liver (99).
Changes in gene expression can be also involved in the
MetR effects (mechanism “ii”). MetR studies found
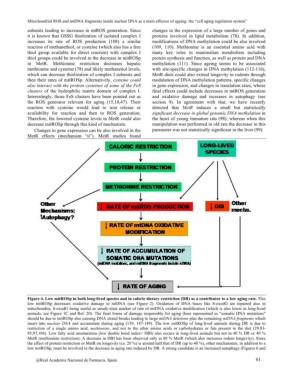
Figure 4. Low mitROSp in both long-lived species and in calorie dietary restriction (DR) as a contributor to a low aging rate. This
low mitROSp decreases oxidative damage to mtDNA (see Figure 2). Oxidation of DNA bases like 8-oxodG are repaired also in
mitochondria, 8-oxodG being useful as steady-state marker of rate of mtDNA oxidative modification (which is also lower in long-lived
animals, see Figure 1C and Ref. 20). The final forms of damage responsible for aging (here represented as "somatic DNA mutations"
should be due to mitROSp also causing DNA strand breaks leading to large mtDNA deletions plus the remaining mtDNA fragments which
insert into nuclear DNA and accumulate during aging (139; 147-149). The low mitROSp of long-lived animals during DR is due to
restriction of a single amino acid, methionine, and not to the other amino acids or carbohydrates or fats present in the diet (29,93-
95,97,104). Low fatty acid unsaturation (low double bond index= DBI) also occurs in long-lived animals but not in 40 % DR or 40 %
MetR (methionine restriction). A decrease in DBI has been observed only at 80 % MetR (which also increases rodent longevity). Since
the effect of protein restriction or MetR on longevity (ca. 20 %) is around half that of DR (up to 40 %), other mechanisms, in addition to a
low mitROSp, must be involved in the decrease in aging rate induced by DR. A strong candidate is an increased autophagy (Figures 6 and
@Real Academia Nacional de Farmacia. Spain 61